Urine Infection
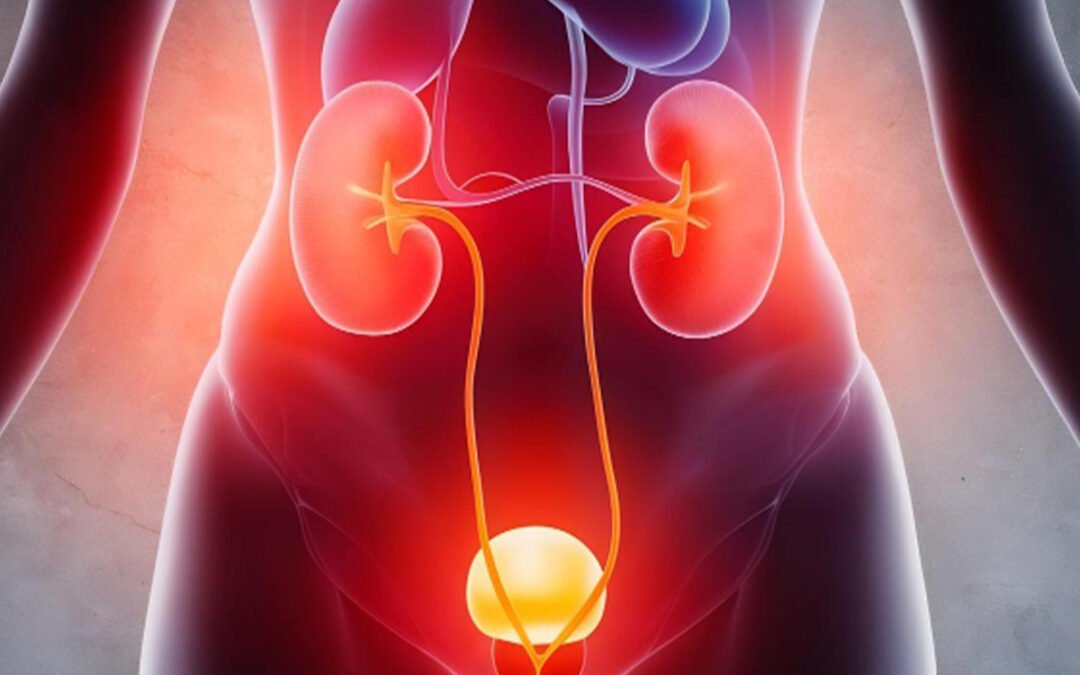
What is Urine Infection ?
Symptoms of Urine Infection
The symptoms of a urine infection depend on which part of the urinary tract is infected. Common signs include:
Strong, persistent urge to urinate
Burning sensation or pain during urination
Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
Blood in urine (hematuria)
Pelvic pain in women (around the pubic bone)
Fever, chills, or back pain (if infection reaches kidneys)
In elderly individuals, UTIs may cause confusion or sudden behavioral changes.
Procedure or Treatment for Urine Infection
Treatment for a urine infection involves:
Diagnosis:
Urine routine and culture tests to identify bacteria
Ultrasound or other scans if recurrent infections occur
Medication:
Antibiotics prescribed based on the infection severity and culture reports
Pain relievers to ease burning or discomfort
Supportive Care:
Drinking plenty of water to flush out bacteria
Avoiding irritant fluids like caffeine and alcohol
Hospitalisation:
Needed in severe kidney infections for intravenous antibiotics
Prevention of Urine Infection
You can prevent UTIs by:
Drinking adequate water daily
Emptying your bladder completely during urination
Wiping front to back after using the toilet
Urinating before and after sexual activity
Avoiding use of irritating feminine products
Wearing cotton underwear and avoiding tight clothing
Benefits of Early Treatment
Prevents spread of infection to kidneys
Relieves pain and discomfort quickly
Reduces risk of recurrent infections
Prevents complications like kidney damage, especially in elderly or diabetic patients
Types of Urine Infections
Cystitis (Bladder Infection): Most common, causes frequent urination and pelvic pain.
Urethritis (Urethra Infection): Causes burning while urinating.
Pyelonephritis (Kidney Infection): Serious infection with fever, back pain, and vomiting, requiring urgent medical care.
