Nephrotic Syndrome
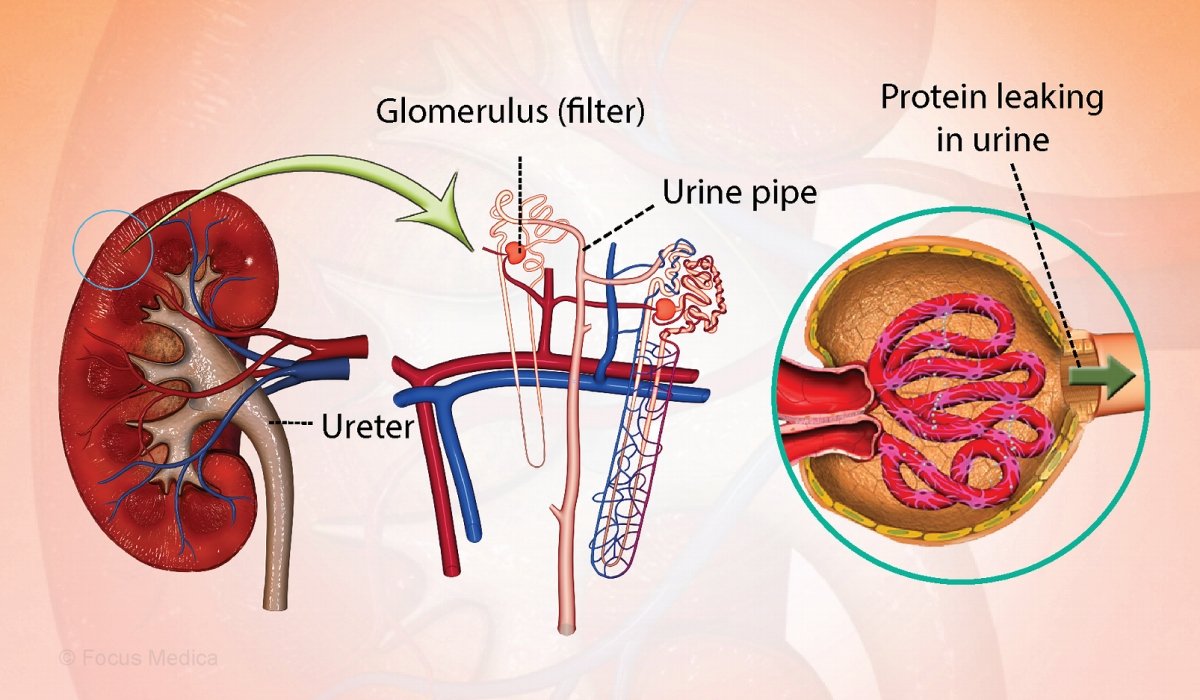
What is Nephrotic Syndrome ?
Symptoms of Nephrotic Syndrome
Swelling (edema) around eyes, feet, and ankles
Foamy or frothy urine due to high protein content
Sudden weight gain due to fluid retention
Fatigue and general weakness
Loss of appetite
High blood pressure in some cases
Causes
Nephrotic Syndrome can be caused by:
Primary kidney diseases (e.g., Minimal Change Disease, Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis, Membranous Nephropathy)
Secondary causes such as diabetes (Diabetic Nephropathy), infections (hepatitis B or C, HIV), certain medications, or systemic diseases like lupus.
Types of Nephrotic Syndrome
Minimal Change Disease (MCD) – most common in children; responds well to steroids.
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) – scarring in parts of the glomeruli; may require advanced treatment.
Membranous Nephropathy – thickening of the glomerular membranes; common in adults.
Secondary Nephrotic Syndrome – due to systemic diseases like diabetes, lupus, infections, or medications.
Diagnosis
Nephrotic Syndrome is diagnosed through:
Urine tests to check for proteinuria
Blood tests for albumin, cholesterol, and kidney function
Kidney biopsy to identify the exact cause in certain cases
Imaging tests like ultrasound to assess kidney structure
Treatment and Management
Treatment aims to reduce symptoms, treat underlying causes, and prevent complications:
Medications:
Corticosteroids (especially in Minimal Change Disease)
Immunosuppressive drugs (cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus) in resistant cases
Diuretics to reduce swelling
ACE inhibitors or ARBs to control blood pressure and reduce proteinuria
Statins for high cholesterol
Dietary changes:
Low salt diet to control edema
Moderate protein intake as per nephrologist advice
Low saturated fat to manage cholesterol
Lifestyle modifications:
Monitoring weight regularly
Avoiding infections by staying updated on vaccinations
Prevention
While some causes cannot be prevented, the risk of kidney damage progression can be reduced by:
Managing diabetes and blood pressure effectively
Avoiding overuse of painkillers (NSAIDs) and nephrotoxic drugs
Maintaining a healthy weight
Eating a balanced, kidney-friendly diet
Regular medical check-ups if you have risk factors or underlying conditions
Benefits of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Prevents permanent kidney damage
Reduces complications like blood clots, infections, and chronic kidney disease
Improves quality of life by managing swelling and fatigue
Enhances long-term kidney function and overall health
